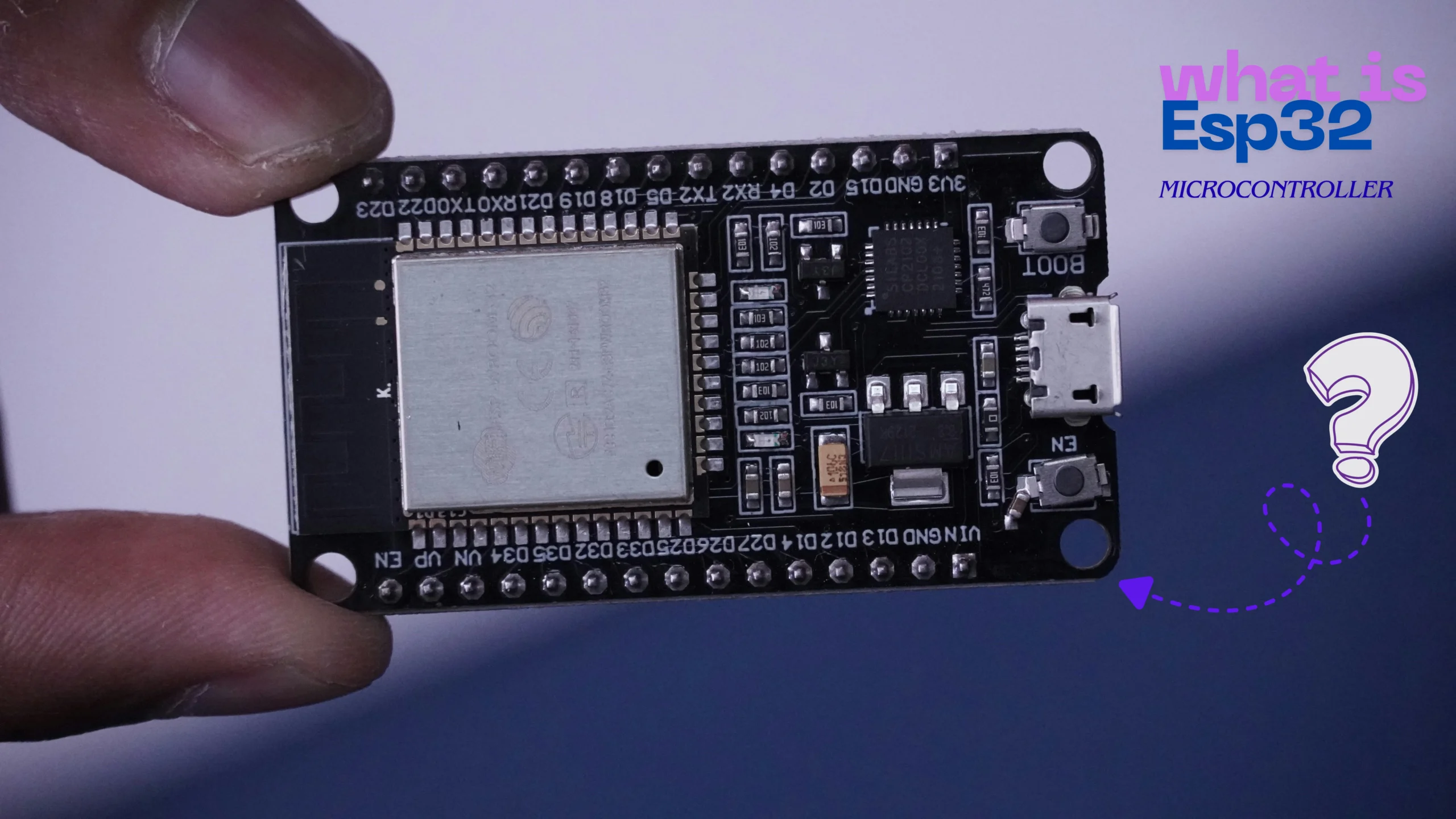
What Is ESP32 Microcontroller? Complete Guide for Beginners (2026)
Imagine a tiny, affordable computer brain that can connect to the internet and talk to other devices without any wires. Sounds like something from a sci-fi movie, right? Well, meet the ESP32 microcontroller! It’s a small but powerful chip that has taken the world of electronics and DIY projects by storm.
If you’ve ever been curious about how smart home devices, weather stations, or even tiny robots work, the ESP32 is often the magic behind them. This complete guide is your friendly starting point. We will break down everything you need to know in simple, easy-to-understand language. Whether you are a total beginner or just looking to understand what all the fuss is about, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the amazing world of the ESP32 microcontroller together!
Also Read This
Types of Cables in Networking (2026): Complete Guide with Examples & Uses
What Is ESP32?
So, what exactly is this ESP32 thing everyone is talking about?
In simple terms, an ESP32 is a tiny, all-in-one computer chip. Think of it as the brain of a small electronic device. It’s designed to process information, follow instructions from a program you write, and control other parts of an electronic project.
The “ESP” part comes from the company that makes it, Espressif Systems. The “32” refers to its 32-bit processor, which just means it’s pretty smart and can handle complex tasks quickly. Unlike the brain in your laptop, the ESP32 microcontroller is a low-power specialist. It’s perfect for devices that need to run on batteries for a long time.
The most amazing feature of the ESP32 is its built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. This means your projects can connect to your home network, send data to the internet, or communicate with your smartphone. This ability to connect wirelessly is what makes the ESP32 a superstar for creating Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It’s like giving your homemade gadgets the same connectivity superpowers as your phone or smart speaker.
ESP32 Features & Specifications
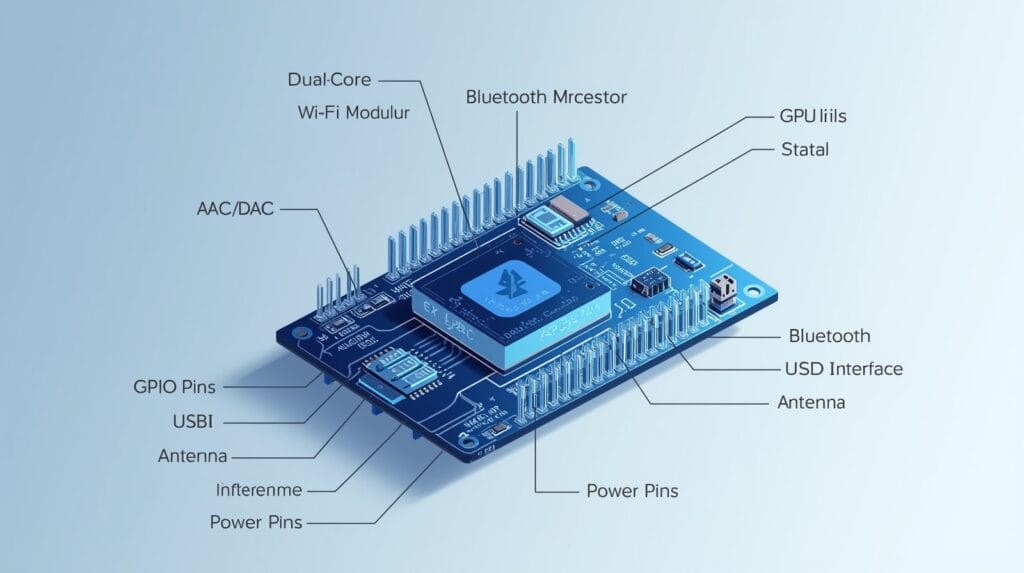
The ESP32 might be small, but it’s packed with features that make it incredibly useful. Let’s look at some of its key specifications. Don’t worry, we’ll explain what these technical terms mean in a simple way!
- Dual-Core Processor: This is a huge deal. Most simple microcontrollers have one brain (core). The ESP32 has two! This means it can do two jobs at the same time. For example, one core could be reading a sensor while the other is sending data over Wi-Fi.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth: The ESP32 has both built-in. The Wi-Fi allows it to connect to your local internet router. The Bluetooth lets it connect to phones, speakers, and other devices directly. You don’t need to buy extra parts for wireless communication.
- Clock Speed: The processor can run at up to 240 MHz. Think of this as how fast the brain can think. A higher speed means it can execute your instructions faster.
- Memory: It has about 520 KB of RAM (for temporary data) and 4 MB of flash memory (for storing your program). It’s not enough for storing movies, but it’s plenty for the code that runs your projects.
- Low Power Consumption: The ESP32 is very efficient. It can be put into “deep sleep” mode where it uses almost no power, making it ideal for battery-powered projects like a soil moisture sensor that only checks the plants once an hour.
- Rich Input/Output (I/O): It comes with many “pins” (the little metal legs on the board). These pins can be used to connect a wide variety of components like sensors, buttons, lights, and motors. We’ll talk more about the pinout in the next section.
- Built-in Sensors (on some models): Some versions of the ESP32 even have built-in sensors for touch (capacitive touch), hall effect (detecting magnets), and temperature.
In short, the ESP32 gives you a powerful, connected, and versatile brain for a very low price, often just a few dollars.
Also Read This
Types of Cables in Networking (2026): Complete Guide with Examples & Uses
ESP32 Pinout Explanation

When you look at an ESP32 development board (like the popular ESP32 DevKit), you’ll see two rows of metal pins on the sides. This is the “pinout.” These pins are how the ESP32 microcontroller talks to the outside world. They are like its hands, ears, and mouth.
Let’s group them to make it easier:
- Power Pins (VIN, 3V3, GND): These are for electricity.
GNDis the ground (negative),3V3provides 3.3 Volts of power, andVINis where you can supply power to the board. - Digital Pins (GPIOs): GPIO stands for General Purpose Input/Output. These pins can be programmed to be either an INPUT (like listening to see if a button is pressed) or an OUTPUT (like turning an LED light on or off). Many of these pins can do special things.
- Analog Pin (ADC): The ESP32 has pins that can read analog signals. Unlike a digital signal (which is just ON or OFF), an analog signal can have a range of values. This is perfect for reading data from sensors like a light sensor or a potentiometer (a dial).
- Special Communication Pins (UART, I2C, SPI): These are for talking to other chips and modules. For example, you can use I2C to connect a screen, or UART to connect a GPS module. They are like special languages for electronics to communicate.
- Other Special Pins: Pins for DAC (to create analog signals), PWM (to simulate analog output, like dimming an LED), and the built-in touch sensors.
You don’t need to memorize all of them! When you start a project, you just look at a pinout diagram to find the pins you need.
Also Read This
Difference Between var let and const in JavaScript (With Examples 2026)
How ESP32 Works?
Understanding how the ESP32 works is simpler than you might think. It’s a three-step process:
- You Write the Code: First, you write a set of instructions (a program) on your computer using a programming language, usually C++ in the Arduino IDE (a free software). This code tells the ESP32 exactly what to do. For example, “Check the temperature sensor. If the temperature is above 30°C, turn on the fan.”
- You Upload the Code: You connect the ESP32 to your computer with a USB cable. Using the software, you “upload” or transfer your code from the computer onto the flash memory of the ESP32 chip. The chip now remembers your instructions.
- It Runs the Program: Once powered on, the ESP32 starts executing your code from the beginning. It runs in a loop, over and over again, constantly checking its inputs (like sensors) and controlling its outputs (like lights or motors). It will keep doing this until you turn it off or upload a new program.
It’s like teaching a dog a new trick. You give the command (the code), and from then on, the dog (the ESP32) performs the trick whenever the right condition is met. The built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are just special tools it can use while following your instructions.
ESP32 Wi-Fi + Bluetooth Features

The wireless features are what make the ESP32 truly special. Let’s break them down.
ESP32 Wi-Fi Capabilities:
The ESP32 isn’t just a Wi-Fi client; it can be a server too!
- As a Station (STA): In this mode, the ESP32 connects to your existing home Wi-Fi network, just like your phone or laptop. Once connected, it can send data to the internet (like posting a sensor reading to a website) or receive commands from anywhere in the world.
- As an Access Point (AP): The ESP32 can create its own Wi-Fi network. Other devices, like your phone, can connect directly to it. This is great for setting up a device without a screen. You connect to its network, open a web page it hosts, and configure its settings.
ESP32 Bluetooth Capabilities:
The ESP32 supports both classic and low-energy Bluetooth.
- Bluetooth Classic (BR/EDR): This is the older, more common type used for streaming audio. You could use it to make a wireless speaker.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): This is a superstar feature for battery-powered projects. BLE is designed for sending small bits of data occasionally without using much power. It’s perfect for fitness bands, smart tags, or a remote sensor that only sends data to your phone when you ask for it.
ESP32 vs Arduino Comparison
If you’re new to electronics, you’ve probably also heard of Arduino. So, what’s the difference? Let’s compare the ESP32 and a typical Arduino Uno.
| Feature | ESP32 | Arduino Uno |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Powerful Dual-Core (up to 240 MHz) | Single-Core (16 MHz) |
| Wireless | Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth | Requires extra “shield” modules (costs more) |
| Memory | ~520 KB RAM, 4 MB Flash | 2 KB RAM, 32 KB Flash |
| Cost | Very Low ($3 – $10) | Low to Medium ($20 – $30) |
| Ease of Use | Slightly more complex to set up | Extremely beginner-friendly |
Which one should you choose?
- Choose an Arduino Uno if you are an absolute beginner who wants to focus purely on the basics of electronics and coding without the added complexity of wireless connectivity. Its simplicity is its strength.
- Choose the ESP32 if your project needs to connect to the internet or a phone, or if you need more processing power. Even as a beginner, if you’re excited about IoT, starting with an ESP32 is a fantastic choice. The community support is huge, and there are countless tutorials to help you.
Think of it like this: Arduino is a reliable bicycle, perfect for learning and short trips. The ESP32 is a scooter with a built-in phone and GPS—it can get you to the same places, but also connect you to a much wider world.
Also Read This
Types of Cables in Networking (2026): Complete Guide with Examples & Uses
Applications / Uses
The ESP32 is so versatile that its uses are almost endless. Here are some common and exciting applications:
- Smart Home Devices: This is a big one. You can build your own smart light switches, thermostat controllers, door locks, and security cameras that you control from your phone.
- Weather Stations: Create a personal weather station that measures temperature, humidity, and air pressure, then sends the data to a website for you to view.
- IoT Sensors: Use the ESP32‘s low-power mode to create sensors that run for months on a battery. Examples include water leak detectors, soil moisture sensors for plants, or mailbox alert systems.
- Wearable Electronics: With its small size and BLE, the ESP32 is great for wearables like a fitness tracker that sends data to your phone.
- Robotics: The dual-core processor is perfect for robots. One core can handle motor control while the other processes data from a camera or ultrasonic sensor.
- Telemetry Systems: It can be used in drones or remote-controlled vehicles to send real-time data like battery voltage and GPS location back to a ground station.
- Industrial Automation: Small-scale automation, like monitoring machine health or controlling a conveyor belt, is also possible with the ESP32.
Best ESP32 Projects for Beginners

Ready to start tinkering? Here are some simple and fun ESP32 projects to get your hands dirty:
- Blink an LED: The “Hello World” of electronics. It teaches you the basics of setting up the software and using a digital output pin.
- Wi-Fi Connected Weather Display: Use the ESP32 to connect to a free weather API on the internet and display the current temperature and forecast on a small screen.
- BLE Door Alert: Create a system where a magnetic switch on your door sends a notification to your phone via Bluetooth Low Energy whenever the door is opened.
- Smart Plant Watering System: Use a soil moisture sensor with your ESP32. Program it to turn on a small water pump automatically when the soil gets too dry. You can even get a notification on your phone.
- Web Server to Control LEDs: Program the ESP32 to create its own Wi-Fi network. When you connect to it, a web page pops up with buttons that allow you to turn LEDs on and off remotely. This teaches you about the Access Point mode.
These projects teach you the core concepts of coding, using sensors, and leveraging the wireless features of the ESP32 microcontroller.
Pros & Cons
Let’s be balanced and look at the good and the not-so-good parts of the ESP32.
Pros:
- Extremely Low Cost: You get a huge amount of power for a very small price.
- Built-in Connectivity: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are included, eliminating the need for extra hardware.
- High Processing Power: The dual-core processor can handle complex tasks much better than many other microcontrollers.
- Vast Community: There is a massive online community. If you have a problem, someone has likely already solved it and posted the solution.
- Low Power Usage: Its efficient power management is perfect for battery-operated projects.
Cons:
- 3.3V Logic Level: Its pins operate at 3.3V, not 5V. Connecting a 5V sensor directly can damage the chip, so you need to be careful or use a logic level shifter.
- Slightly Steeper Learning Curve: While still beginner-friendly, it can be a bit more complex to set up initially compared to an Arduino Uno.
- Limited Analog Pins: While it has some, the number of true analog input pins is smaller than the number of digital pins.
FAQs
Q1: Is ESP32 better than Arduino?
It’s not about being strictly “better.” The ESP32 is more powerful and has built-in Wi-Fi/BT, making it superior for connected projects. Arduino is simpler and better for pure beginners learning electronics fundamentals without distractions.
Q2: Can I program ESP32 with Arduino IDE?
Yes, absolutely! This is one of the best parts. You can use the familiar and free Arduino IDE to write and upload code to the ESP32, making the transition from Arduino very smooth.
Q3: What programming language is used for ESP32?
The most common language used with the Arduino IDE is C++. You can also use MicroPython, which is a version of Python designed for microcontrollers, if you prefer that language.
Q4: How much does an ESP32 board cost?
ESP32 development boards are incredibly cheap. You can typically find them online for anywhere between $3 to $10, depending on the specific model and features.
Q5: Is ESP32 good for beginners?
Yes! While it has a slight learning curve, its low cost, powerful features, and massive community support make it an excellent choice for beginners, especially those interested in Internet of Things (IoT) projects from the start.
Also Read This:)
Best 10 AI Tools for Coding in 2026 – Write Code Faster with Artificial Intelligence
Conclusion
The ESP32 microcontroller is one of the most powerful and beginner-friendly boards available today, offering Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, fast processing, and endless project possibilities. Whether you are learning IoT, building smart devices, or experimenting with sensors, the ESP32 gives you everything in a single compact board. Its flexibility, low cost, and advanced features make it an ideal choice for students, hobbyists, and developers in 2026. If you want to explore embedded systems or start your IoT journey, the ESP32 is the perfect place to begin.